err_name_not_resolved Error Fix – Solve & Get Online!

By Aravindhan | August 8, 2023
You’re Eagerly typing in the URL of a website you’ve been meaning to visit, excitedly waiting for the page to load, only to be met with a frustrating error message: “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED.” The ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error is a common issue encountered by internet users when trying to access a website. This error occurs when the DNS (Domain Name System) fails to resolve the website’s IP address. If you’re facing this frustrating error, don’t worry! In this article, we will explore 10 proven methods to fix the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error and get you back online.
What does the error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” mean?”
If you’re receiving the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error message, the browser is not found the IP address which matches the domain name you have entered. Without the correct IP address, your browser cannot establish a connection with the website server and the page is inaccessible.
This error can occur on your Chrome browsers whether you’re using it on a PC (Windows, macOS, or Linux) or a mobile device Android or iOS. Also, this error is not limited to Chrome browser, you can also face this error on other browsers like Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge.
ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED: 10 Methods to fix it
Method 1: Clear Your Browser Cache and Cookies
Your browser’s cache and cookies can accumulate outdated or corrupted data related to websites you’ve visited. This can lead to conflicts in DNS resolution, resulting in the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Clearing cache and cookies removes this stored data, allowing your browser to collect fresh information from websites.
In some cases, misconfigured or problematic cookies can interfere with the DNS resolution process, causing the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Clearing cookies removes these potential errors and enables a clean browsing session.
To fix the error, try clearing your browser’s cache and cookies. Below are the steps for removing browser cache and cookies for popular browsers:
- How to clear browsing data in Chrome:
In addition to clearing cache and cookies, checking specific settings in Google Chrome can help resolve the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Clearing browser cache and cookies in Google Chrome is a simple process. Follow the below steps to clear cache and cookies:
Go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Clear Browsing Data.
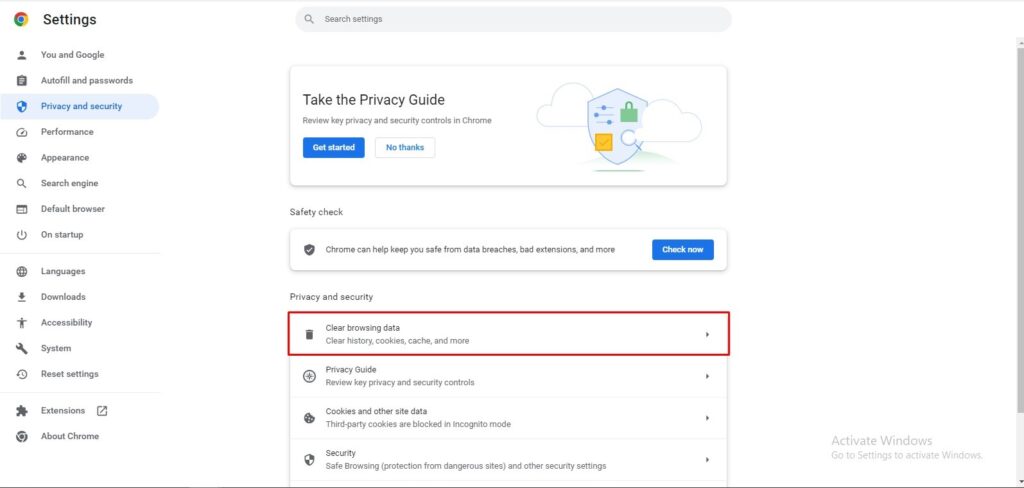
Make sure that you have selected the “All time” option under “Time range”, otherwise it will only delete your most recent browser history. Once selected, click “Clear data”.

- How to clear browsing data in Firefox:
The ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error can disturb your browsing experience, but by clearing your browser’s cache and cookies in Mozilla Firefox, you can often resolve the issue. Clearing cache and cookies eliminates outdated or corrupted data, misconfigured cookies, and cache conflicts, enabling your browser to establish accurate DNS resolution. By following the below steps, you can solve the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error and enjoy a smoother browsing experience in Mozilla Firefox.
Go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Clear Data.

Uncheck the box for “Cookies and Site Data” and click “Clear.”

- How to clear browsing data in Microsoft Edge:
Following the below steps, you can solve the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error and enjoy a smoother browsing experience in Microsoft Edge.
Go to Settings > Privacy, search, and Services> Choose what to clear.

Goto Privacy, search, and services.
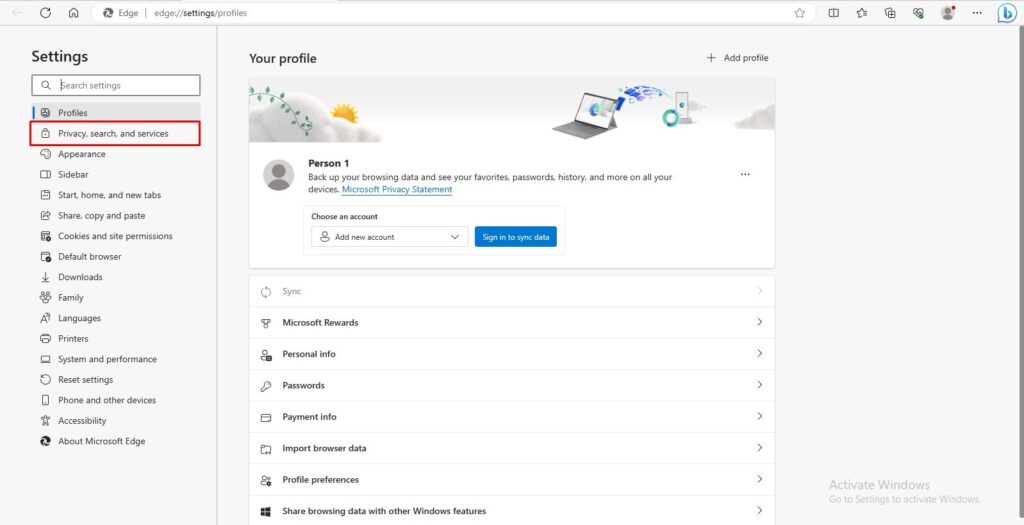
Here, scroll down until you see the Choose what to clear button, and then click on it.
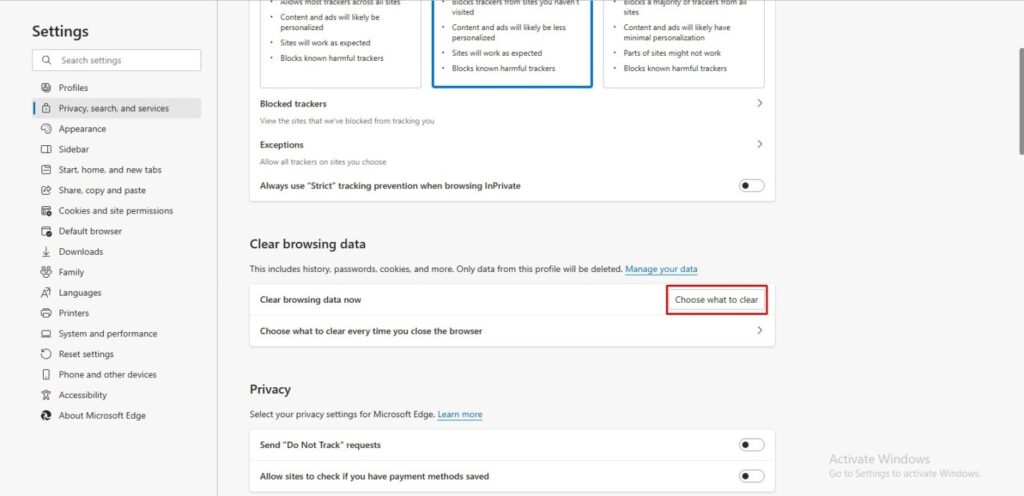
Make sure to set the time range to All time and Click Clear now.
ALSO READ: What does DNS Translates a Domain Name Into?
Method 2: Flush DNS Cache
Flushing the DNS cache on your device is a recommended troubleshooting step for resolving the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. By removing the DNS cache, you remove any potentially outdated or corrupted DNS records, allowing your device to get the latest information from the DNS servers. Flushing the DNS cache can help in the following situations:
Outdated cache entries: The DNS cache on your device may store outdated records for various websites. Flushing the cache ensures that you obtain the most up-to-date IP addresses associated with domain names.
DNS server changes: If the DNS server changes, it can result in the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Flushing the DNS cache prompts your device to retrieve new DNS information from a different server.
Incorrect records: In some cases, incorrect DNS records can be stored in the cache, leading to the name resolution failure. Flushing the cache clears out these erroneous entries and allows for a fresh DNS lookup.
Flushing the DNS cache can help resolve any conflicts or outdated information that might be causing the error. Follow these steps to flush DNS in the most common ways:
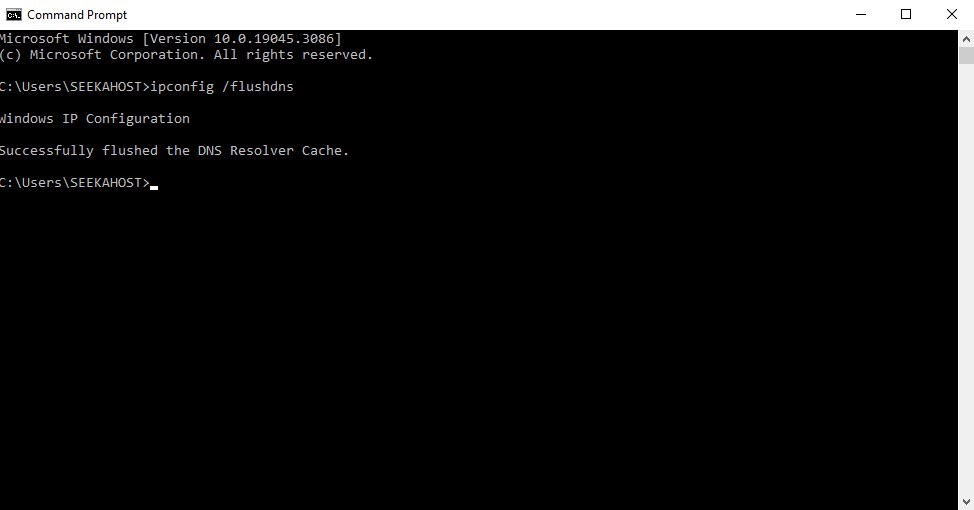
Right-click on the Windows icon, then select Search.
- Type cmd in the search box and select Command Prompt.

- Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
Method 3: Change DNS Servers
Switching to a different DNS server can often solve the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Consider using public DNS servers like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or OpenDNS (208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220). Below are a few benefits of changing DNS servers,
Improved reliability: Some DNS servers may experience downtime or have slow response times, leading to intermittent connectivity issues. Switching to a more reliable DNS server can ensure consistent access to websites and reduce the occurrence of the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Enhanced security: Certain DNS servers offer additional security features, such as built-in malware and phishing protection. By choosing a reputable DNS server, you can minimize the risk of accessing malicious websites and improve your overall online security.
Faster browsing speeds: Some DNS servers are optimized for performance and offer faster response times, resulting in quicker website loading. By switching to a faster DNS server, you can enhance your browsing experience and reduce delays associated with the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Here’s how to change DNS servers:
Right-click on the Windows icon, then select Search.
Type Control Panel and click the result to open it.
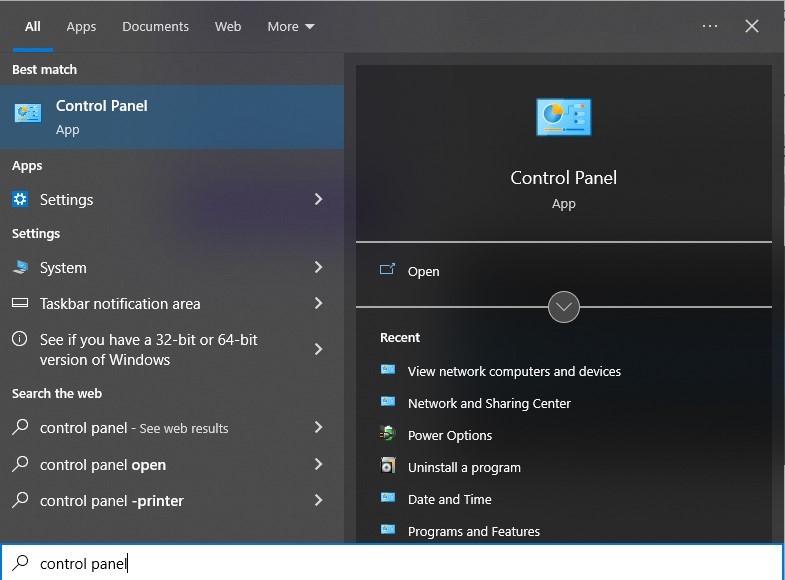
- Select Network and Internet

- Go to Network and Sharing Center

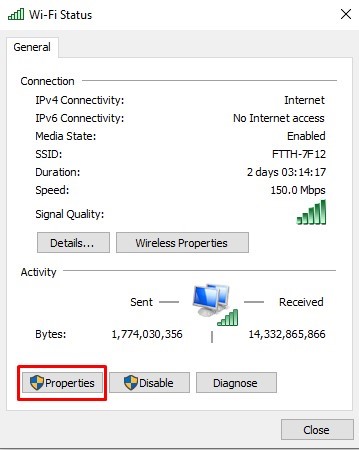
Select your active network connection and click on Properties.
- Choose “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click on Properties.
- Select “Use the following DNS server addresses” and enter the “preferred DNS server addresses.”
If you’re using macOS, below are the steps:
- Open System Preferences and select Network.
- Click on Advanced and open the DNS tab.
- Click the + and add a new DNS server.
- Type the public DNS servers.
- Click OK and click Apply on the prompt window.

Method 4: Disable Proxy Settings
Disabling proxy settings can be an effective troubleshooting step to resolve the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Below are some reasons that can help for disabling proxy settings,
Misconfigured proxy settings: Incorrectly configured proxy settings can interfere with the DNS resolution process, leading to the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Disabling proxy settings eliminates the possibility of misconfigurations of domain names.
Proxy server issues: Proxy servers may experience downtime, have connectivity problems, or be misconfigured themselves. Disabling proxy settings allow your device to directly connect to websites, bypassing potential issues with the proxy server and resolving the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error.
Network restrictions: In workplaces or educational institutions, proxy settings may be enforced to restrict access to specific websites. Disabling proxy settings can help you to access the websites that were previously inaccessible.
How to Disable Proxy Settings:
Proxy settings can sometimes interfere with DNS resolution, leading to the error. Below are the steps to Disable Proxy Settings.
Windows:
a. Press the Windows+ R, type “inetcpl.cpl”, and press Enter to open the Internet Properties dialog box.
b. Go to the “Connections” tab and click on “LAN settings.”
c. Uncheck the box next to “Use a proxy server for your LAN” and ensure that the “Automatically detect settings” option is selected.
d. Click “OK” to save the changes.
macOS:
a. Open “System Preferences” and click on “Network.”
b. Select your active network connection and click on “Advanced.”
c. Navigate to the “Proxies” tab and uncheck all the boxes under “Select a proxy server to configure.”
d. Click “OK” to save the changes.
Method 5: Check Hosts File
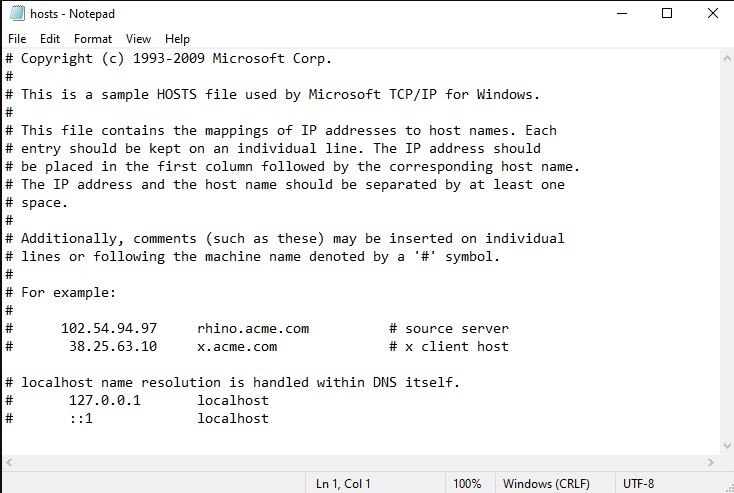
The host file is a plain-text file on your computer that maps domain names to IP addresses. It acts as a local DNS resolver, allowing you to manually specify IP address associations for specific domain names. The host’s file on your computer can override DNS resolutions and lead to the error. By ensuring there are no incorrect entries in the host’s file, you can eliminate this potential cause.
By default, the host’s file is located in the following directory:
Windows:
- C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
macOS:
- /etc/hosts
Linux:
- /etc/hosts
ALSO READ: What is 127.0.0.1 localhost and Loopback Address?
To check and fix the hosts file, follow the below steps:
a. Open a text editor with administrative privilege (On Windows, you can use Notepad as an administrator by right-clicking on it and selecting “Run as administrator.”)
b. Navigate to the directory (as mentioned above).
c. Open the host file in the text editor.
d. Look for any entries that may be causing conflicts or containing incorrect information. In most cases, valid entries should have an IP address followed by one or more domain names. Incorrect entries might have typos, missing IP addresses, or conflicting associations.
e. If you find any suspicious or incorrect entries, Delete them or add a “#” at the beginning of the line.
f. Save the changes.
After that Close and restart your web browser to ensure the changes take effect.
Method 6: reset the Winsock catalog
When encountering the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error, one potential solution is to reset the Winsock catalog. The Winsock catalog is a crucial component of the Windows operating system that manages network communication through various protocols. To perform this reset, you can follow these steps:
Right-click on the Windows icon, then select Search.
- Type cmd in the search box
- Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator“
- In the command prompt window, type the following command and press Enter: “netsh winsock reset“
- Wait for the process to complete. Once finished, you will see a message indicating that the Winsock catalog has been successfully reset.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Resetting the Winsock catalog can help resolve connectivity issues associated with the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error. It clears any corrupted or misconfigured settings related to network communication, allowing your system to establish proper connections and resolve domain names correctly. After performing this reset, try accessing the website again to check if the error persists.
Method 7: Disable Antivirus or Firewall Temporarily
Antivirus and firewall software are designed to protect your computer from malicious activities by monitoring network traffic and blocking potentially harmful connections. However, these security measures can occasionally block legitimate connections, including DNS resolution, resulting in the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Temporarily disabling your antivirus or firewall software can help identify if they are causing the issue and allow you to access the desired websites.
Remember to re-enable them after troubleshooting.
Method 8: Test Using a Different Internet Connection
Testing your device’s connection with a different network allows you to determine if the error is specific to your current internet connection or if it persists across different networks.
If the error does not occur when using a different internet connection, it suggests that the issue lies with your original network, and further troubleshooting can be done accordingly.
Method 9: Restart Your Router
Sometimes, the issue lies with your router or modem. Restarting the router can refresh its settings and resolve any temporary glitches causing the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error. Simply power off your router waits for a few seconds, and then power it back on.
Method 10: Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
If none of the previous methods have resolved the error, it may be necessary to reach out to your ISP for assistance. They can investigate and resolve any underlying issues with your internet connection that are causing the error.
Conclusion:
Encountering the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error can be frustrating, but with these 10 proven methods, you can troubleshoot and resolve the issue effectively. Remember to try each method one at a time and test if the error persists before moving on to the next. By following these steps, you’ll be back to browsing the web smoothly in no time.
Note: If the error persists after trying these methods, it is advisable to contact your internet service provider (ISP) for further assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]:
- What does the error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” mean?
The error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” typically appears in web browsers when the DNS (Domain Name System) lookup fails to resolve the IP address of a website. It means that your browser is unable to establish a connection to the server hosting the website you’re trying to access.
- Why am I encountering the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error?
There can be various reasons for this error to occur:
- DNS configuration issues: Incorrect DNS settings or misconfigured DNS records can lead to the error.
- Internet connectivity problems: Unstable or intermittent internet connection can result in failed DNS resolution.
- Firewall or security software: Overly restrictive firewall settings or security software can block DNS requests.
- DNS server problems: Issues with the DNS server you are using can prevent proper resolution of domain names.
- Can the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error be specific to a certain device or browser?
The error can occur on any device or browser that relies on DNS resolution for internet connectivity. It is not specific to a particular device or browser.
- Can the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error be website-specific?
Yes, while the error is typically associated with DNS resolution problems, it can also be triggered by specific websites. It could indicate issues with the website’s DNS configuration or server. However, if the error persists with multiple websites, the problem is likely on your end.
- How can I change DNS servers?
You can change DNS servers by accessing your network settings and modifying the DNS server address. Consider using public DNS services like Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1).
ALSO READ: How to Configure Cloudflare DNS for a Domain?
- Are there any alternative error codes related to DNS resolution issues?
Yes, there are several other error codes that relate to DNS resolution problems, such as “DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN,” “ERR_NAME_RESOLUTION_FAILED,” or “DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_BAD_CONFIG.” These errors share similarities with “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” and may require similar troubleshooting steps.
- Why should I restart my computer?
A simple restart can sometimes resolve temporary glitches or conflicts on your system. It helps refresh the network settings and clears any lingering issues that might be causing the error.
- Where is the host’s file located?
The host file is a system file that can override DNS lookups. Its location varies depending on the operating system:
For Windows: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
For Mac: /private/etc/hosts
- What should I do if none of the suggested solutions fix the error?
If you have exhausted all the recommended troubleshooting steps and the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error persists, consider seeking professional assistance. Contact your ISP, a network specialist, or a technical support team to investigate the issue further and provide specialized guidance for your specific situation.